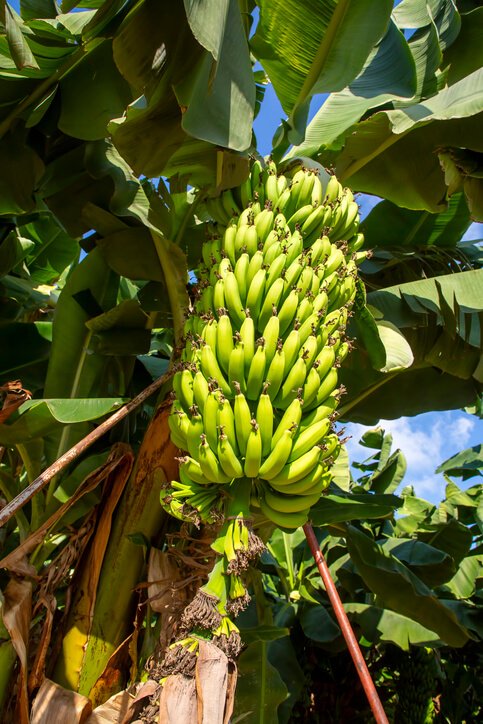
Hi there! I am thrilled to welcome you to today’s exploration into a topic that holds both fascination and importance, and that’s Wild Bananas!
Often overshadowed by their cultivated counterparts, boast incredible diversity. These resilient plants have adapted to a myriad of environments, showcasing a captivating range of shapes, sizes, and flavors that reveal the untamed beauty hidden within the vast wilderness.
The Roots and Habitat
To truly understand wild bananas, we must trace their roots back to their origins. These resilient plants have evolved over centuries, adapting to different climates, terrains, and environmental conditions. Whether nestled in the dense rainforests of Southeast Asia or thriving in the open savannas of Africa, wild bananas have carved a niche for themselves in diverse landscapes.
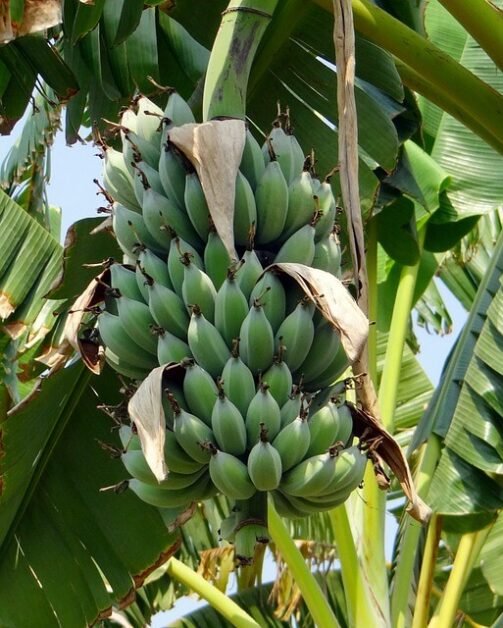

As we delve into the natural habitats of bananas, we uncover their ecological significance. These plants play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity, acting as guardians of genetic wealth. Their ability to thrive in different environments contributes to the delicate balance of ecosystems, making them an integral part of the natural world.
Nutritional Insights
Beyond their aesthetic allure, those little bananas conceal nutritional potency that goes beyond the ordinary.
These fruits, more than just a feast for the taste buds, are a treasure trove of essential vitamins, minerals, and unique compounds that contribute to a diverse and nutrient-packed diet. Explore the hidden depths of nutritional richness that bring to the table.
While specific nutritional information for wild bananas may vary based on the species and variety, here’s a general overview of the nutritional content you might find in wild bananas:
1. Calories:
- Wild bananas, like their cultivated counterparts, are a relatively low-calorie fruit. On average, a medium-sized banana contains around 105 calories.
2. Carbohydrates:
- Rich source of carbohydrates, mainly in the form of natural sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. Carbohydrates provide a quick and easily digestible energy boost.
3. Dietary Fiber:
- Like cultivated ones, contain dietary fiber. Fiber supports digestive health, promotes a feeling of fullness, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. A medium-sized banana typically provides around 3 grams of fiber.
4. Vitamins:
- Wild bananas are a good source of various vitamins. They are particularly rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant that supports the immune system, and vitamin B6, which plays a role in brain development and function.
5. Minerals:
- Potassium is a standout mineral in bananas, including wild varieties. This mineral is crucial for heart health, muscle function, and maintaining proper fluid balance in the body.
6. Antioxidants:
- Like cultivated bananas, wild bananas contain antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals in the body. These antioxidants contribute to overall health and may have a role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
7. Natural Sugars:
- The natural sugars found in wild bananas provide a sweet taste and a quick, healthy energy boost. The presence of fiber helps regulate the absorption of these sugars, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
8. Protein and Fat:
- Bananas, including wild varieties, are low in both protein and fat. While they are not significant sources of these macronutrients, they offer essential energy and nutrients in other forms.
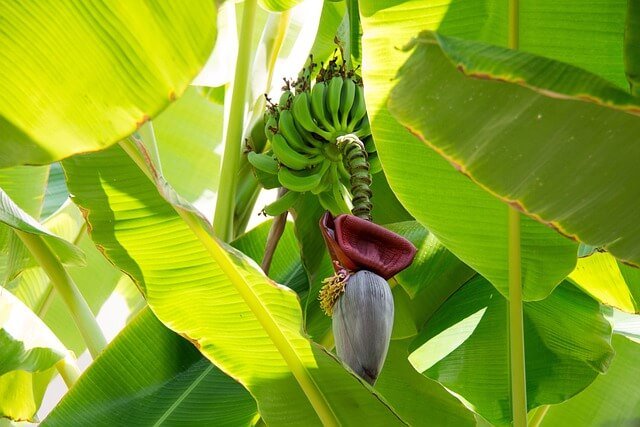

The Future of Wild Bananas
Contemplate the future role of wild bananas in the realm of sustainable agriculture. As we confront evolving challenges such as pests and diseases, the genetic diversity harbored by wild bananas becomes paramount. Explore how harnessing this diversity may hold the key to cultivating resilient banana varieties, ensuring the longevity of these precious plants in the agricultural landscape of tomorrow.
The differences between Wild Bananas and Cultivated Bananas
The difference between wild bananas and cultivated bananas lies in their origin, genetic diversity, size, appearance, flavor profile, commercial availability, and susceptibility to diseases. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Botanical Origin:
- Wild Bananas: Original, undomesticated banana species that grow naturally in the wild without human intervention.
- Cultivated Bananas: Domesticated bananas that have undergone selective breeding for desirable traits.
2. Genetic Diversity:
- Wild Bananas: Exhibit a wide range of genetic diversity with numerous species, resulting in different sizes, shapes, colors, and flavors.
- Cultivated Bananas: Lack the same genetic diversity. Commercially available bananas typically belong to a few selected varieties.
3. Size and Appearance:
- Wild Bananas: Vary significantly in size, appearance, and taste. Can be small and stout or large and slender, with colors ranging from red and green to purple.
- Cultivated Bananas: Tend to be larger and more uniform in size and appearance. The common cultivated banana is the elongated, yellow Cavendish variety.
4. Flavor Profile:
- Wild Bananas: Offer diverse flavor profiles. Some may have a sweeter taste, while others could be more tangy or have unique flavor notes.
- Cultivated Bananas: The flavor of commercially available bananas, such as the Cavendish, is generally sweet with a creamy texture.
5. Commercial Availability:
- Wild Bananas: Not commercially available in standard grocery stores. Often consumed locally where they grow naturally.
- Cultivated Bananas: Widely available in grocery stores. The Cavendish variety dominates commercial banana cultivation.
6. Resistance to Diseases:
- Wild Bananas: Tend to have natural resistance to certain diseases and pests, contributing to their survival in their native habitats.
- Cultivated Bananas: The widely cultivated Cavendish variety is susceptible to certain diseases, and its uniformity makes it more vulnerable to widespread issues.
7. Human Intervention:
- Wild Bananas: Have evolved naturally without significant human intervention.
- Cultivated Bananas: Have been selectively bred and cultivated by humans for desirable characteristics such as size, taste, and disease resistance.
8. Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Wild Bananas: Hold cultural and historical significance as the original banana varieties that early humans encountered and utilized.
- Cultivated Bananas: Have become a staple food in many cultures worldwide, contributing to dietary diversity and economic importance.
Understanding these distinctions helps highlight the diverse nature of bananas and the impact of human cultivation on shaping the characteristics of the bananas we commonly consume today.